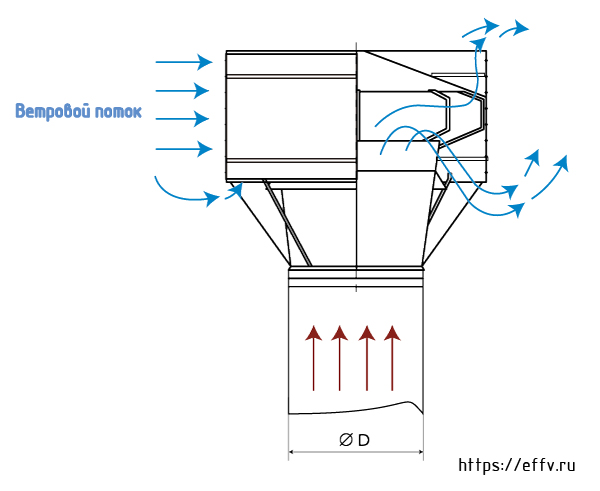
Raschyot Deflektora Cagi
Trachyandra divaricata (Jacq.) Kunth Enum.Pl. 4:580 (1843) Conservation Code: Not threatened Naturalised Status: Alien to Western Australia Name Status: Current Brief Description Grazyna Paczkowska, Wednesday 22 June 1994. Rhizomatous, perennial, herb, to 0.35 m high. White, Aug to Nov. White or grey sand. Coastal dunes. View Tommy Chism’s full profile. Your colleagues, classmates, and 500 million other professionals are on LinkedIn. View Tommy’s Full Profile. Tommy Chism’s Activity.
Abstract Pro-apoptotic Bax and Bak have been implicated in the regulation of p53-dependent apoptosis. We assessed the ability of primary baby mouse kidney (BMK) epithelial cells from bax −/−, bak −/−, and bax −/− bak −/− mice to be transformed by E1A alone or in conjunction with dominant-negative p53 (p53DD). Although E1A alone transformed BMK cells from p53-deficient mice, E1A alone did not transform BMK cells from bax −/−, bak −/−, or bax −/− bak −/− mice. Thus, the loss of both Bax and Bak was not sufficient to relieve p53-dependent suppression of transformation in epithelial cells. Software oscilloscope free download. To test the requirement for Bax and Bak in other death signaling pathways, stable E1A plus p53DD-transformed BMK cell lines were derived from the bax −/−, bak −/−, and bax −/− bak −/− mice and characterized for their response to tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-mediated apoptosis. Otveti na ekzamenacionnie bileti operatora koteljnoj. The loss of both Bax and Bak severely impaired TNF-α-mediated apoptosis, but the presence of either Bax or Bak alone was sufficient for cell death.
Cytochrome c was released from mitochondria, and caspase-9 was activated in Bax- or Bak-deficient cells in response to TNF-α but not in cells deficient in both. Thus, either Bax or Bak is required for death signaling through mitochondria in response to TNF-α, but both are dispensable for p53-dependent transformation inhibition. Apoptosis can be initiated in transformed cells by an intrinsic mechanism when deregulation of the cell cycle initiates an apoptotic response mediated by the tumor suppressor p53.
Apoptosis can also be initiated by an extrinsic mechanism when TNF-α 1 or Fas ligand initiates an apoptotic response mediated by death receptors. When the adenovirus E1A oncogene stimulates proliferation during transformation, the cellular response is apoptosis mediated by p53 (,). Activation of p53 results in altered transcription of a wide variety of genes that are involved in many facets of cell metabolism, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis (, ). Genes transcriptionally up-regulated by p53 that have been implicated in promoting apoptosis include the Bcl-2 family members bax, bak, puma, and noxa (). Evidence suggests that Bax and Bak function is required for the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytosol during apoptosis (, ). Cytochrome c release from the mitochondria occurs in many apoptotic signaling pathways including those implemented by p53 and TNF-α ().